3D Scanning Applications. What is a 3D scanner used for?
What are 3D Scanning Applications for? A 3D scanner is useful in applications where: 1) You rely on having accurate 3D measurements in making important decisions 2) You need to capture vast amount of surface measurements quickly and efficiently 3) Need to reconstruct a physical object in 3D to be visualize digitally on screen
3D Scanning Applications
Documentation and Archiving

Having a digital reproduction of an artifact ensures that if anything happens to the original there is still a digital record of the past.
3D scanners help preserve history by capturing delicate artifacts and fossils into 3D digital form. Non-contact 3D scanners, such as structured-light systems, are especially great for this type of application because they capture the object without causing any disturbance to the original.
This technology empowers museums to archive their collections digitally and share them on the computer with anyone around the world.
Product Development and Design
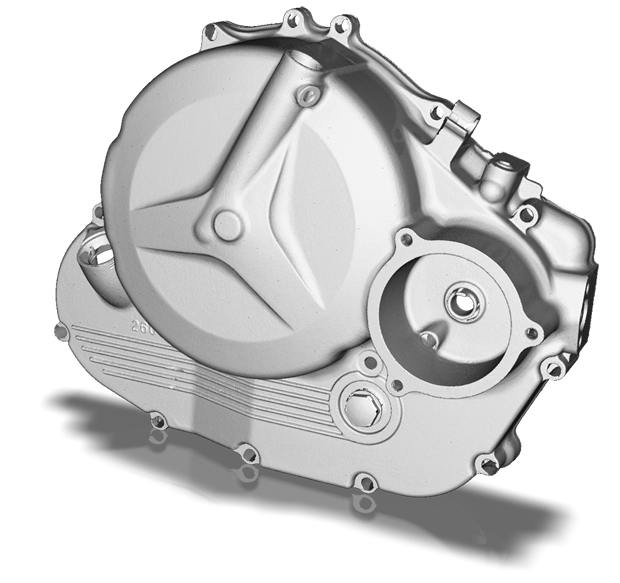

Old automotive parts with no original CAD can use reverse engineering to create new documentation for manufacturing.
Reverse engineering refers to the process of analyzing the construction of an existing product in order to develop a similar or improved design. It’s a quest to investigate and understand the designer’s motivation behind how and why the product was created in this particular way (known as design intent).
Instead of designing from a blank slate, it’s easier to use existing objects as a reference for the new design with reverse engineering. There are also times when the original CAD drawings of a design is no longer available but documentation is essential to manufacture the product. By scanning the object with a 3D scanner, you get all the surface measurements you need to analyze its construction. It’s much easier to understand design intent to recreate or improve on the design. The process of creating CAD from 3D scan data is known as Scan to CAD.
Want to learn more about Scan to CAD? Read Reverse Engineering 101: Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Parametric CAD from 3D Scan Data
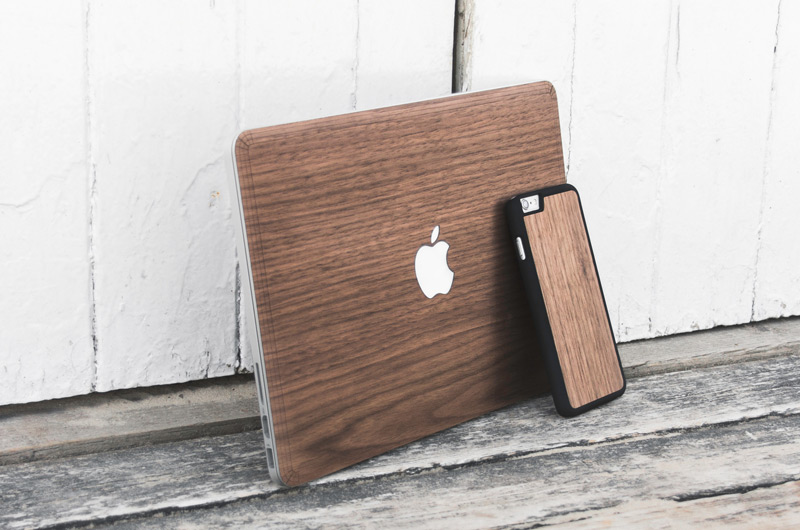

Creating Accessories for Hardware
Taking measurements using hand tools to create cases for laptops and phones is a tedious task and yields inaccurate results. It’s much easier to get precise and accurate measurements quickly with a 3D scanner.
3D scanning is the most efficient and cost-effective way to design complementary products. For example, when designing accessories for hardware such as a case for a cell phone, you can scan the phone using a 3D scanner to get surface dimensions (with millions of measurement points) to design a protective shell. Because the case needs to be an exact fit, having accurate measurements of the phone is important to the fit of the case.
Quality Inspection
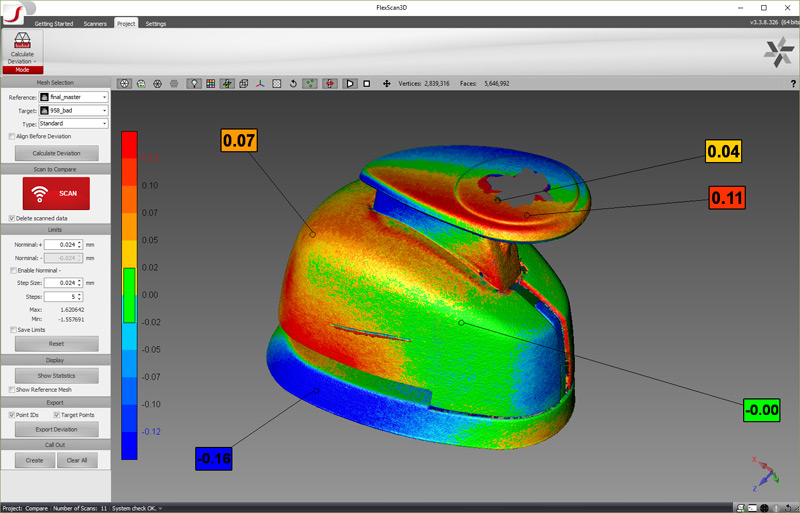
Deviation Analysis
Quickly determine if a manufactured part is within tolerance by comparing the CAD model against the part’s measurements captured with a 3D scanner.
3D scanners’ ability to get 3D measurements of complex and freeform shapes with accuracy and precision make them an ideal solution for quality inspection applications. By compare CAD model with surface measurements of the manufactured object captured by a 3D scanner, companies can determine if the product is within manufacturing tolerance to reduce product defects.
Create Custom Products
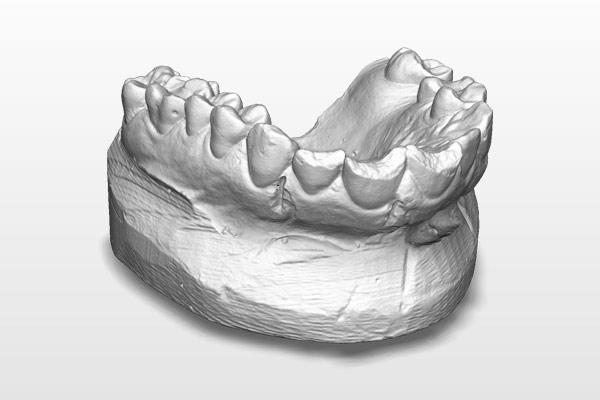
Create Dental Products Such as Crowns
By 3D scanning dental impressions or tooth, you get precise and accurate measurements of the patient’s mouth to create dental products that provides custom fit for comfort.
A 3D scanner can acquire patient’s body measurements quickly for creating customized medical products. When it comes to creating one-off customized products for patients, manufacturing products using 3D scanning and 3D printing technologies greatly reduce manufacturing costs compared to traditional methods of manufacturing.
Custom products include:
- Dental: Braces, retainers, and mouth guards
- Face: Form-fitted face mask for treating burn victims
- Body Parts: Making prosthetics (i.e. arm, leg, back)
Robotic vision and guidance
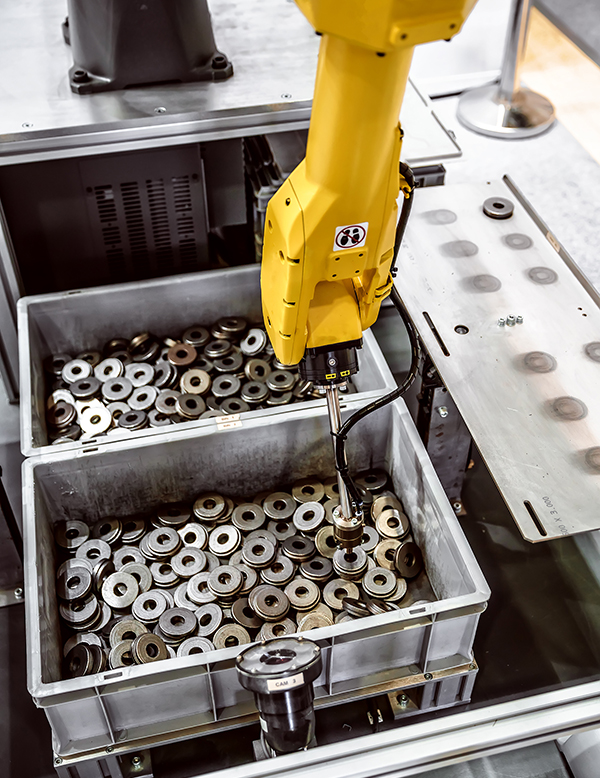

For Vision-Guided Robotics (VGR) applications in a factory setting, 3D scanners play an instrumental role in providing visual 3D information necessary for controlling robotic motion such as:
- pick and place: identify and locate parts without any human interaction (i.e. picking parts from one bin and placing them into another location).
- creating a closed loop system so that you can see the results of the robot’s actions.
- reacting to dynamic changes in the robot’s workspace.
- Inspecting manufactured parts against CAD model for quality assurance (i.e. 3D scanners are integrated into production facilities to create a fully automated robotic 3D inspection cell.)
The benefits to using structured-light 3D scanners for VGR systems:
- Fast: They are fast at generating and processing 3D data in order to make real-time decisions.
- Simple: Just like a 2D camera except in 3D. No external hardware interfaces or devices required.
- Flexible: They can be easily setup to work with different kinds of robots from small to big.
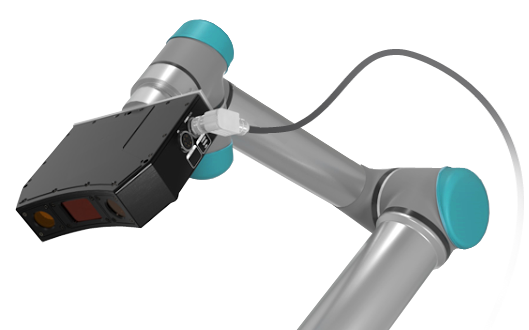
VGR systems help companies improve productivity while reducing costs. The benefits of VGR systems include:
- Cost savings: VGR systems are efficient at performing redundant tasks compared to humans, which improves productivity.
- Improve product quality: Robots with 3D vision are more accurate at performing mundane tasks than humans when doing it manually. Staff can focus on maintaining systems and more challenging work.
Research
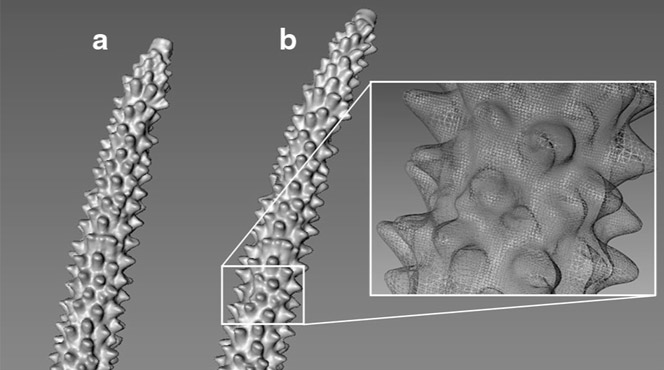
Measuring living corals using a 3D scanner to monitor how they change over time.
Research article: Effects of light and elevated pCO(2) on the growth and photochemical efficiency of Acropora cervicornis
scanner.A digital 3D model contains dense and accurate surface measurements of an object. It’s extremely useful for research when comparing specimens to see how they are different from one another or how a specimen changes over time.
